Kotlin Collection 정리
01 Oct 2022패스트 캠퍼스 실무 프로젝트로 배우는 Kotlin & Spring 강의 정리
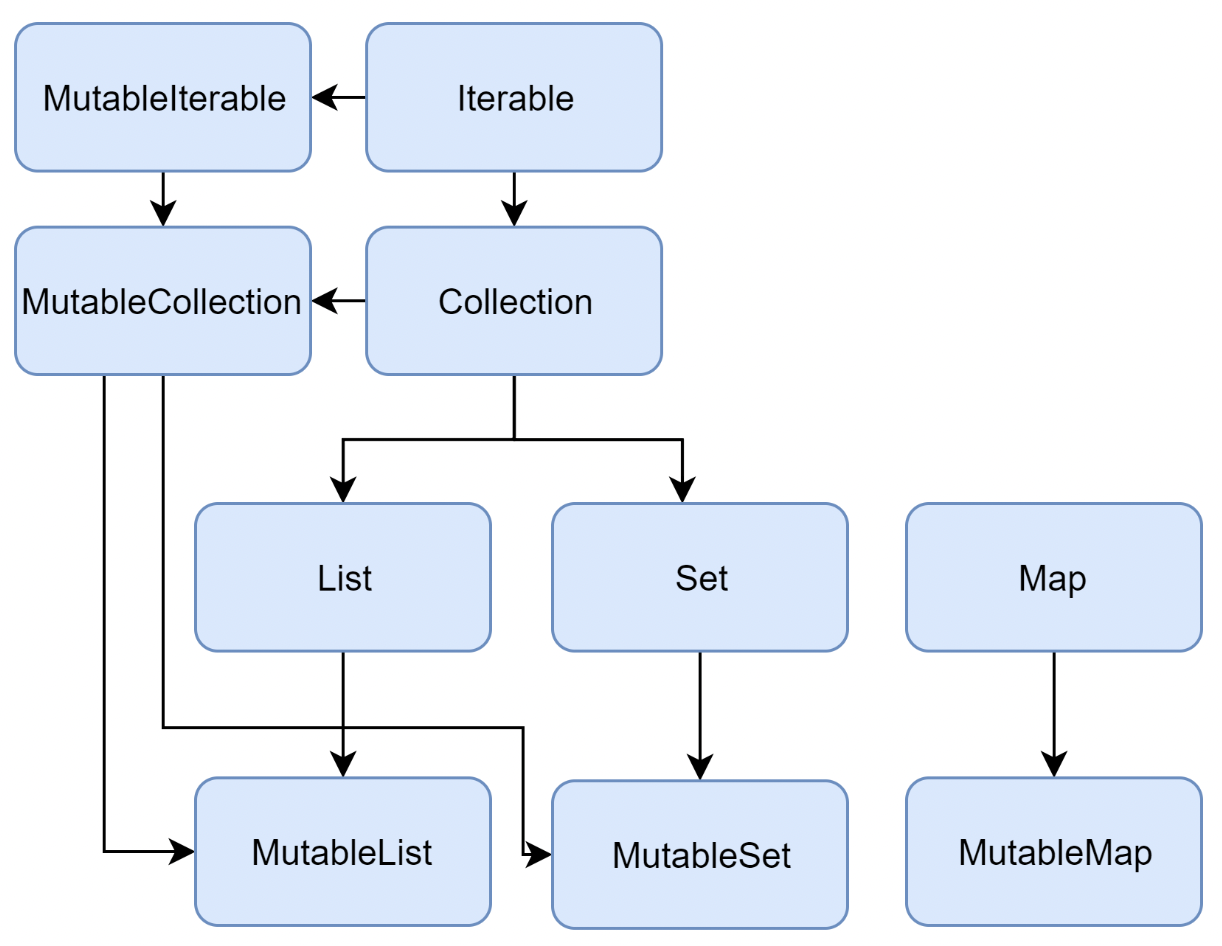
Colletion
- 코틀린 표준 라이브러리에서 제공하는 기본 콜렉션 타입:
List,Set,Map - 종류
- 불변(Immutable): 읽기 전용 컬렉션
- List, Set, Map
- 가변(Mutable): 삽입, 수정, 삭제와 같은 쓰기 작업이 가능한 컬렉션
- MutableList, MutableSet, MutableMap
import java.util.*
fun main() {
// immutable
val currencyList = listOf("dollar", "euro", "won")
// mutable
val mutableCurrencyList = mutableListOf<String>().apply {
add("dollar")
add("yuan")
add("won")
}
// immutable set
val numberSet = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
// mutable set
val mutableNumberSet = mutableSetOf<Int>().apply {
add(1)
add(2)
add(3)
}
// immutable map
val numberMap = mapOf("one" to 1, "two" to 2, "three" to 3)
// mutable map
val mutableNumberMap = mutableMapOf<String, Int>().apply {
set("one", 1)
set("two", 2)
set("three", 3)
}
mutableNumberMap["four"] = 4
// collection builder
// 내부에서는 Mutable 이지만 반환할 때 Immutable 타입
val numberList: List<Int> = buildList {
add(1)
add(2)
add(3)
}
// linkedList
val linkedList = LinkedList<Int>().apply {
addFirst(1)
add(2)
addLast(4)
}
// arrayList
val arrayList = ArrayList<Int>().apply {
add(1)
add(2)
add(3)
}
// iterater
val iterator = currencyList.iterator()
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
println(iterator.next())
}
// for loop
for (currency in currencyList) {
println("currency = ${currency}")
}
// forEach & lambda
currencyList.forEach { println(it) }
currencyList.forEach(::println)
// map inline function
val currencyList = listOf("dollar", "euro", "won")
val upperList = lowerList.map { it.uppercase() }
// filter
val filteredList = upperList.filter { it == "A" || it == "C" }
// sequence
// terminal operator 동작한 후에 list 생성하게 됨
val sequenceExample = upperList
.asSequence()
.filter { it == "A" }
.filter { it == "B" }
.filter { it == "C" }
.toList()
}